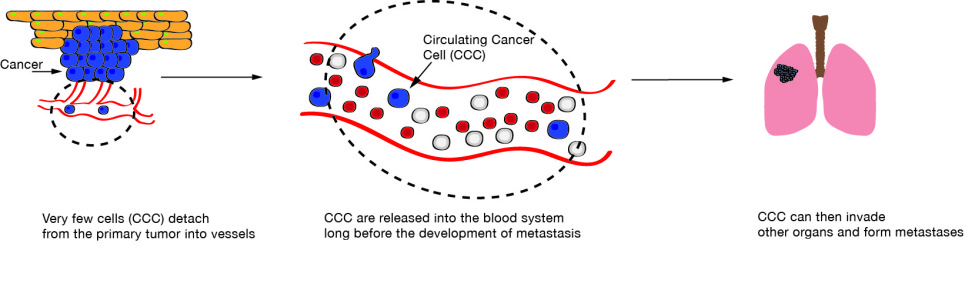
Circulating Cancer Cells (CCC) are cells that have detached from the primary tumor and are circulating in the bloodstream (initial phase of tumor invasion). CCC are not only very rare and fragile, they are also of different types, some of them much more invasive than others. Moreover, they are not the only rare cells in the blood, as other non-tumor cells, deriving from organs, may be present.
CCC could cause metastases, and circulate in blood for months, or even years, before metastasis formation. Therefore, they provide an amazing tool to identify patients at risk of developing metastases.
It has been a real challenge to develop a method allowing the isolation without loss of all types of CCC from the blood of patients, irrespectively of the type of solid cancer, while preserving the integrity of CCC. ISET® has proven it can overcome this challenge. It is the only method, based on blood filtration, to have been clinically validated.
Since CCC are isolated from blood by ISET®, a Cytopathologist can examine and identify them. Cytopathology is the only diagnostic and reference method in Oncology to identify tumor cells; it has been validated and used to diagnose cancer for over 150 years.
Furthermore, since tumor cells are the target of anti-cancer drugs, CCC can be used to determine whether a given treatment is effective or not, as an effective treatment leads to their disappearance. CCC can be also genetically analyzed to guide the choice of the most suited targeted anticancer treatments. Finally, since invasive tumors start spreading CCC when these tumors are still tiny and not detectable by imaging, CCC can help detect an invasive tumor at a very early stage. Just like an infection, cancer has a much higher chance to be cured if it is diagnosed at a very early stage of tumorous invasion.